Application of ultra-high performance convergence chromatography-tandem quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry in the analysis of Span composition
-
摘要:
采用超高效合相色谱串联四极杆飞行时间质谱(UPCC-QTOF-MS)检测方法,建立定性分析药用辅料司盘组成的方法。采用VIRIDIS HSS C18 SB 100A 色谱柱 (3.0 mm×150 mm,18 μm),以CO2和异丙醇-四氢呋喃(98∶5)为流动相,梯度洗脱,柱温为50 ℃,流速为1 mL/min,以异丙醇-0.1%甲酸水溶液(8∶2)为补偿溶剂,背压为13.78 MPa,离子化模式为ESI+,采集模式为MSE,扫描范围m/z 100~
1200 ,分别测定司盘20、40、60、80、85样品。 建立的方法可区分不同牌号司盘间组成差异,对各司盘组分进行定性分析,其中司盘20可分析得到21种组分,司盘40可分析得到7种组分,司盘60可分析得到13种组分,司盘80可分析得到9种组分,司盘85可分析得到9种组分,并根据各组分质谱图开展了结构分析。本研究建立的方法可区分不同牌号司盘间的组成差异,同时也可用于分析不同牌号的司盘组成及结构,此方法绿色环保,对司盘质量控制、工艺评价、制剂应用选择等具有指导意义。-
关键词:
- 超高效合相色谱串联四极杆飞行时间质谱 /
- 司盘 /
- 组成分析
Abstract:A method for the qualitative analysis of the composition of pharmaceutical excipient Span was established by ultra-high performance convergence chromatography-tandem quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPCC-QTOF-MS). The separation was performed on a VIRIDIS HSS C18 SB 100A column (3.0 mm×150 mm, 18 μm) with gradient elution using CO2 and isopropanol-tetrahydrofuran (98∶5) as the mobile phase. The column temperature was 50 °C. The flow rate was 1 mL/min. Isopropanol and 0.1 % formic acid aqueous solution (8∶2) were used as the compensation solvent. The back pressure was 13.78 MPa. The ionization mode was ESI +, the acquisition mode was MSE, and the m/z scanning range was from 100 to 1200. The samples of Span 20, 40, 60, 80 and 85 were determined respectively. The established method could distinguish the composition differences between different brands of Span, and it could analyze the components of different brands of Span as well. 21 components could be analyzed by Span 20, 7 by Span 40, 13 by Span 60, 9 by Span 80, and 9 by Span 85, and the structural analysis of each component was carried out. The method established in this paper can distinguish the composition differences between different brands of Span. It can also be used to analyze the composition and structure of different brands of Span. This method is green and environmentally friendly with guiding significance for Span quality control, process evaluation, and preparation application selection, etc.
-
司盘是脂肪酸与山梨坦反应生成的失水山梨醇脂肪酸酯的一类物质,是常用的亲脂型非离子表面活性剂,具有较强的乳化、分散和润滑等作用。常见的工艺主要为山梨醇与脂肪酸直接酯化或脱水山梨醇(山梨坦)与脂肪酸在催化条件下酯化 [1−3]。根据原料中脂肪酸碳链长度的不同,可划分为不同牌号,目前中国药典收载了5个牌号的司盘,分别为司盘20、40、60、80和85[4]。司盘广泛应用于食品、化妆品及医药等各个领域。在化学制剂中,司盘主要作为乳化剂等,用于乳膏剂等;在生物制品中,司盘则可作为疫苗佐剂等用于注射剂中 [5−10]。
脂肪酸为生产司盘的原料之一,因其为混合物,其中可能含有多种长度碳链的饱和及不饱和脂肪酸,因此司盘也含有多种脂肪酸;合成司盘的另一原料山梨醇为多元醇,其脱水产物复杂多样,可能得到1,4-去水山梨醇、1-5-去水山梨醇等[11],这些失水山梨醇均可与脂肪酸发生酯化反应,同时也可能生成单酯、二酯和三酯,因此司盘并非单一组成、结构明确的简单化合物,而为结构复杂的混合物。对于酯类化合物,其脂肪酸碳链长度、双键数量、分布组成情况均可能影响其最终理化性质,从而影响制剂功能性、安全性[12]。随着近年来制剂研发的不断深入,复杂药用辅料被越来越广泛地应用于各类制剂中,亟须高效的分离分析手段对其基本的物质组成进行研究,以考察影响复杂药用辅料应用的关键质量属性,有助于开展质量控制等工作。目前各国药典虽均收载了多个牌号的司盘,但均未收载此类品种鉴别项,也未收载组成分析相关项目;当采用的高效液相色谱等分析方法对混合物等复杂药用辅料进行分析时,多需采用多根色谱柱串联、延长分析时间等方式达到组分分离,且分离效果可能也并不尽如人意,而此类方法也无法得到复杂药用辅料的组分信息,因此,有必要建立适宜的分析方法,对司盘进行分离,以得到各个组分的组成信息,为辅料生产、使用、制剂研发企业等在选择、应用司盘时提供质量控制的方法。
超高效合相色谱串联四极杆飞行时间质谱结合了超临界流体色谱和超高效液相色谱的技术特点及优点,不仅可缩短分析时间,也可提高分离效果,同时还减少了溶剂的用量,更为绿色环保,近年来也越来越多地用于各类混合物、药品及复杂药用辅料分析中[13−24]。本研究根据司盘理化性质特点,结合查阅的相关文献参考,建立了超高效合相色谱串联四极杆飞行时间质谱(UPCC-QTOFMS)对司盘组分的分离分析方法,方法有效、可行,有助于帮助各生产应用单位更好地开展司盘质量控制等工作。
1. 材 料
1.1 仪 器
电子天平(美国梅特勒公司);气相色谱仪(美国安捷伦公司);超高效合相色谱串联四极杆飞行时间质谱仪(UPCC-QTOFMS,美国沃特世公司);液相色谱柱:VIRIDIS HSS C18 SB 100A(3.0 mm×150 mm,18 μm);气相色谱柱: DB-FFAP (30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm);Millipore超纯水系统。
1.2 试剂与药品
正己烷、无水甲醇、氢氧化钾、三氟化硼甲醇溶液、氯化钠、无水硫酸钠、亚麻酸甲酯、异丙醇、乙腈、氢氧化钠溶液、四氢呋喃、0.1%甲酸水溶液(均为市售试剂),己酸甲酯、辛酸甲酯、癸酸甲酯、月桂酸甲酯、十四烷酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、棕榈油酸甲酯、硬脂酸甲酯、油酸甲酯(均为中国食品药品检定研究院对照品),亚油酸甲酯(USP对照品),CO2 、N2(均>99.99%,市售气体),甲酸及亮氨酸脑啡肽(均由美国沃特世公司提供)。司盘20、40、60、80及85样品均由辅料生产企业赠送;试剂级司盘80由厂家F生产,两批不同工艺司盘80由厂家W提供。
2. 方 法
2.1 脂肪酸组成测定
按《中华人民共和国药典》(2020年版)四部各司盘标准中收载的脂肪酸组成检查项下方法测定各牌号司盘脂肪酸组成。
2.1.1 对照品溶液制备
取己酸甲酯、辛酸甲酯、癸酸甲酯、月桂酸甲酯、十四烷酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、棕榈油酸甲酯、硬脂酸甲酯、油酸甲酯、亚油酸甲酯、亚麻酸甲酯适量,以正己烷配制成各脂肪酸甲酯质量浓度约为1 mg/mL的混合溶液作为定位用对照品溶液。
2.1.2 供试品溶液制备
取各司盘样品0.2 g,加入0.5 mol/L氢氧化钾甲醇溶液8 mL,65 ℃水浴回流10 min,放冷,加入三氟化硼甲醇溶液10 mL,65 ℃水浴回流2 min,放冷,加入正己烷10 mL,65 ℃水浴回流1 min,放冷,加饱和氯化钠溶液20 mL,摇匀静置分层,取上层,经无水硫酸钠干燥过滤,即得供试品溶液。
2.1.3 色谱条件
以DB-FFAP(30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm)色谱柱测定,初始柱温150 ℃,维持3 min,以5 ℃/min的速率升至220 ℃,维持3 min;载气为高纯氮气,载气流速为1 mL/min,进样口温度为240 ℃,分流比为10∶1,采用FID检测器,其温度为280 ℃。
2.1.4 测定法
分别取对照品溶液及供试品溶液1 μL,注入气相色谱仪,记录色谱图,以面积归一化法计算各脂肪酸含量。
2.2 UPCC- QTOFMS测定
2.2.1 供试品溶液制备
以异丙醇-四氢呋喃(95∶5)为溶剂,分别配制质量浓度约为0.003、0.5、1及3 mg/mL的各牌号司盘供试品溶液;通过结果确定适宜的考察浓度后,配制各牌号司盘供试品溶液。
2.2.2 重复性考察
取司盘20,按“2.1.1”项下方法制备成质量浓度约为3 mg/mL供试品溶液,连续进样6次,记录并对比6次总离子流图,考察方法重复性。
2.2.3 稳定性考察
取司盘85按“2.1.1”项下方法制备成质量浓度约为3 mg/mL供试品溶液,于室温放置4 d后,记录并对比各总离子流图,考察溶液稳定性。
2.2.4 不同司盘间对比
按“2.2.1”项下方法制备不同牌号质量浓度约为3 mg/mL的辅料司盘供试品溶液、F厂家生产的司盘80及W厂家生产的两批不同工艺的司盘80供试品溶液,分别开展对比考察。
2.2.5 色谱条件
采用Waters VIRIDIS HSS C18 SB 100A (3.0 mm×150 mm,18 μm)色谱柱,柱温为50 ℃,以异丙醇-0.1% 甲酸水溶液(8∶2)为补偿溶剂,补偿溶剂流速为0.3 mL/min。以A (CO2)和B(异丙醇-四氢呋喃,95∶5)为流动相,A、B起始比例为95∶5,其中A在 3 min时调整为90,8 min时调整为85,12 min时调整为80,18min时调整为70,21 min时调整为95,并保持至23 min;流动相流速为1 mL/min。
2.2.6 质谱条件
离子化模式:电喷雾离子源正离子模式(ESI+);雾化气温度:450 °C ;雾化气流速 :900 L/h;源温度:120 °C;毛细管电压:3 kV;锥孔电压:40 V;采集模式:MSE;扫描范围:m/z 100~
1200 。2.2.7 测定法
配制200 pg/mL的亮氨酸脑啡肽的乙腈-水(1∶1)溶液,对质谱调谐,取供试品溶液1 μL,以0.5 mmol/L的甲酸钠的异丙醇-水(9∶1)溶液作为内标,注入UPCC- QTOFMS,记录总离子流图,并采用MassLynx v4.1软件对总离子流图的各个主要峰进行质谱提取。
3. 结 果
3.1 脂肪酸组成测定结果
各牌号司盘脂肪酸组成测定结果如表1所示。
Table 1. Determination results of fatty acid composition of each brand of SpanName of fatty acids Normalization results/% Span 20 Span 40 Span 60 Span 80 Span 85 Methyl caproate 0.1 / / / / Methyl caprylate 4.7 / / / / Methyl decanoate 5.4 / / / / Methyl laurate 52.5 / / 0.12 / Methyl myristate 19.9 / / 0.29 2.8 Palmitic acid methylester 9 99 47.1 4.97 4.3 Methylcis-9-hexadecenoate / / / / 4.8 Methyl stearate 5.3 / 48 1.54 1.1 Methyl oleate / / / 79.28 70.8 Methyl linolenate 2 / / 13.23 12.9 3.2 UPCC- QTOFMS测定结果
3.2.1 结构分析
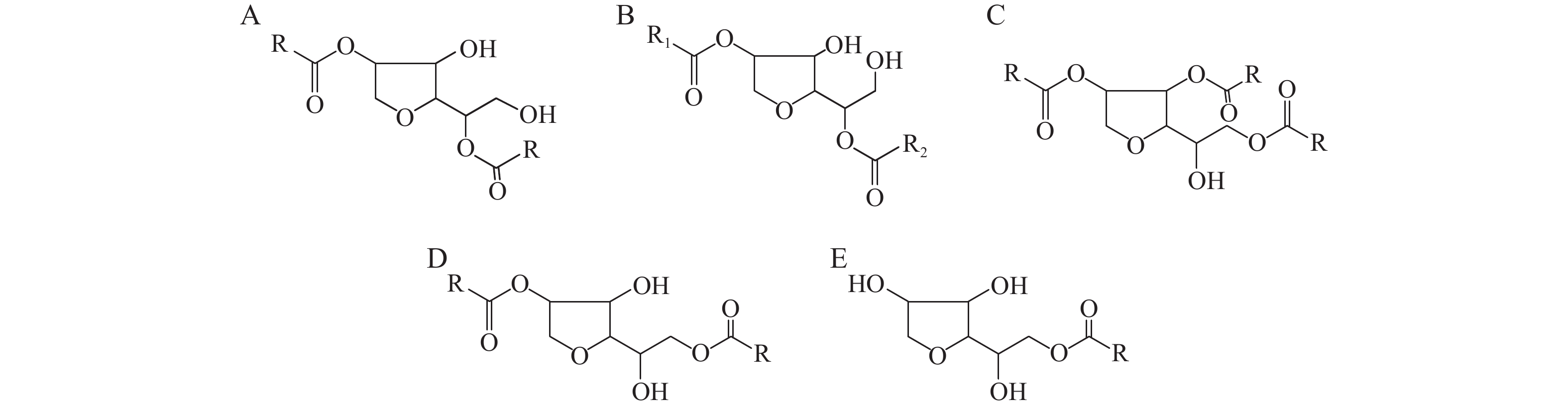
仅当样品质量浓度为3 mg/mL时可得到理想的总离子流图,可提取各主峰质谱图用于分析结构,结合表1中各牌号司盘所含的脂肪酸种类,对各主峰进行归属。根据山梨醇结构,确定司盘中可能存在的5种母核结构,见图1,以此为基础推断各司盘结构,结果见表2–表6。
Table 2. Span 20 structure speculationNo. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 477.29 A Octanoic acid root,laurate root or decanoate root,laurate root 2 505.32 A Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,laurate root 3 533.35 A Decanoate root,myristic acid root or laurate root,laurate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root 4 561.39 A Laurate root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,palmitate root or octanoic acid root,stearate root 5 589.42 A Decanoate root,stearate root or laurate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,myristic acid root 6 351.19 B Laurate root and H 7 379.22 B Myristic acid root and H 8 733.53 C Octanoic acid root,decanoate,stearate root or octanoic acid root,laurate,palmitate or octanoic acid root,myristic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate,decanoate,palmitate or decanoate,laurate,myristic acid root or laurate,laurate,laurate 9 435.28 A Stearate root 10 789.59 C Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root,stearate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root,palmitate root or decanoate root,laurate root,stearate root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,palmitate root or laurate root,laurate root,palmitate root or laurate root,myristic acid root, myristic acid root 11 495.3 D Octanoic acid root,laurate root or decanoate root,decanoate root 12 523.33 D Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,laurate root 13 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 14 551.36 D Decanoate root,myristic acid root or laurate root,laurate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root 15 579.39 D Octanoic acid root,stearate root or decanoate root,palmitate root or laurate root,myristic acid root 16 607.42 D Decanoate root,stearate root or laurate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root ,myristic acid root 17 635.45 D Laurate root,stearate root or myristic acid root,palmitate root 18 313.14 E Octanoic acid root 19 341.17 E Decanoate root 20 369.2 E Laurate root 21 397.23 E Myristic acid root Table 3. Span 40 structure speculationNo. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 2 393.27 E Myristic acid root 3 901.71 C Myristic acid root,palmitate root,stearate root,laurate root,stearate root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root,palmitate root 4 791.53 C Octanoic acid root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,linoleic acid root or laurate root,laurate root,linoleic acid root 5 663.48 D Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root 6 425.26 E Palmitate root 7 631.50 A Laurate root,linoleic acid root Table 4. Span 60 structure speculationNo. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 673.51 A Palmitate root, stearate root 2 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 791.53 C Octanoic acid root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,linoleic acid root or laurate root,laurate root,linoleic acid root 3 701.54 A Stearate root,stearate root C Octanoic acid root,octanoic acid root,linoleic acid root 4 435.28 B Stearate root and H 847.59 C Decanoate root,stearate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,oleate root,oleate root or laurate root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root 5 645.48 A Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root or aurate root,stearate root,stearate root 6 901.71 C Palmitate root,palmitate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,palmitate root,stearate root 7 929.74 C Myristic acid root,stearate root ,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root,stearate root 8 663.49 D Palmitate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,stearate root 9 985.80 C Stearate root,stearate root,stearate root 10 957.78 C Palmitate root,stearate root ,stearate root C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root 11 425.26 E Palmitate root 12 691.52 D Palmitate root,stearate root 13 719.55 D Stearate root,stearate root Table 5. Span 80 structure speculationNo. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 671.49 A Oleate root,palmitate root A Linoleic acid root,linoleic acid root 2 695.49 A Oleate root,linoleic acid root D Oleate root,stearate root or stearate root,linoleic acid root 3 697.51 A Oleate root,oleate root D Stearate root,stearate root 4 431.25 B Linoleic acid root and H 5 433.27 B Oleate root and H 6 977.74 C Stearate root,linoleic acid root ,linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root 7 979.76 C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root ,oleate root,oleate root 8 715.52 D Oleate root,oleate root stearate root,linoleic acid root 9 713.5 D Oleate root,linoleic acid root Table 6. Span 85 structure speculationNo. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 643.46 A Myristic acid root,oleate root or palmitate root ,palm oil acid root 2 669.48 A Palmitatet,linoleic acid root or palm oil acid root ,oleate root 3 695.49 A Oleate root,linoleic acid root D Oleate root, stearate root 4 697.51 A Stearate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root ,oleate root D Stearate root 5 433.27 B Oleate root and H 6 715.52 D Stearate root,Linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root 7 979.76 C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root,oleate root 8 953.74 C Palmitate,stearate root ,linoleic acid root or palmitate root,oleate root,oleate root or palm oil acid root,oleate root,stearate root C Oleate root,linoleic acid root,linoleic acid root 9 641.45 A Myristic acid root,linoleic acid root D Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root 3.2.2 精度考察
连续进样司盘20供试品溶液6次,各次总离子流图基本一致,认为方法重复性良好。
3.2.3 稳定性考察
司盘85供试品溶液于室温放置4 d前后,总离子流图未见明显变化,认为溶液稳定性良好。
3.2.4 不同司盘间对比考察
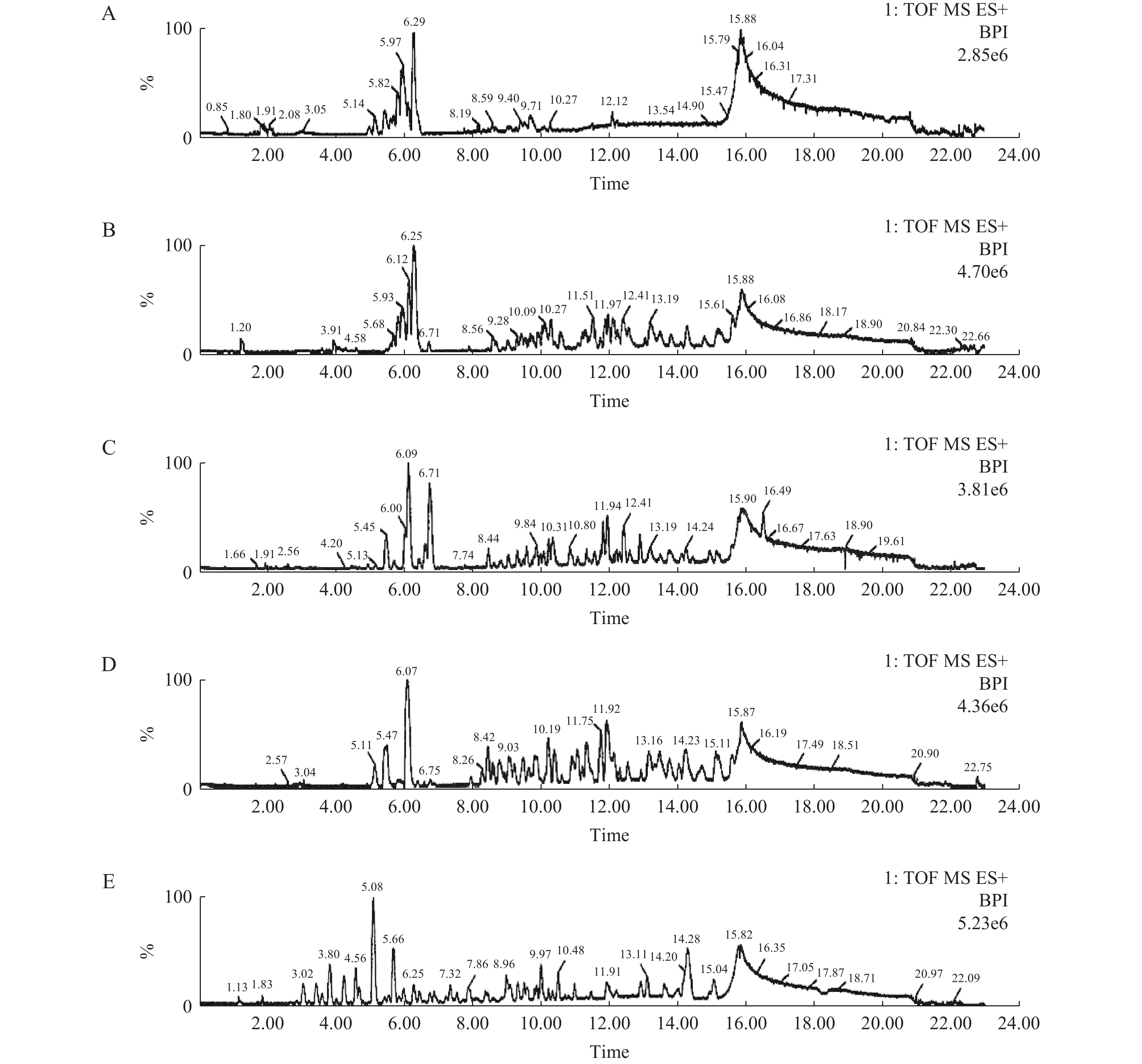
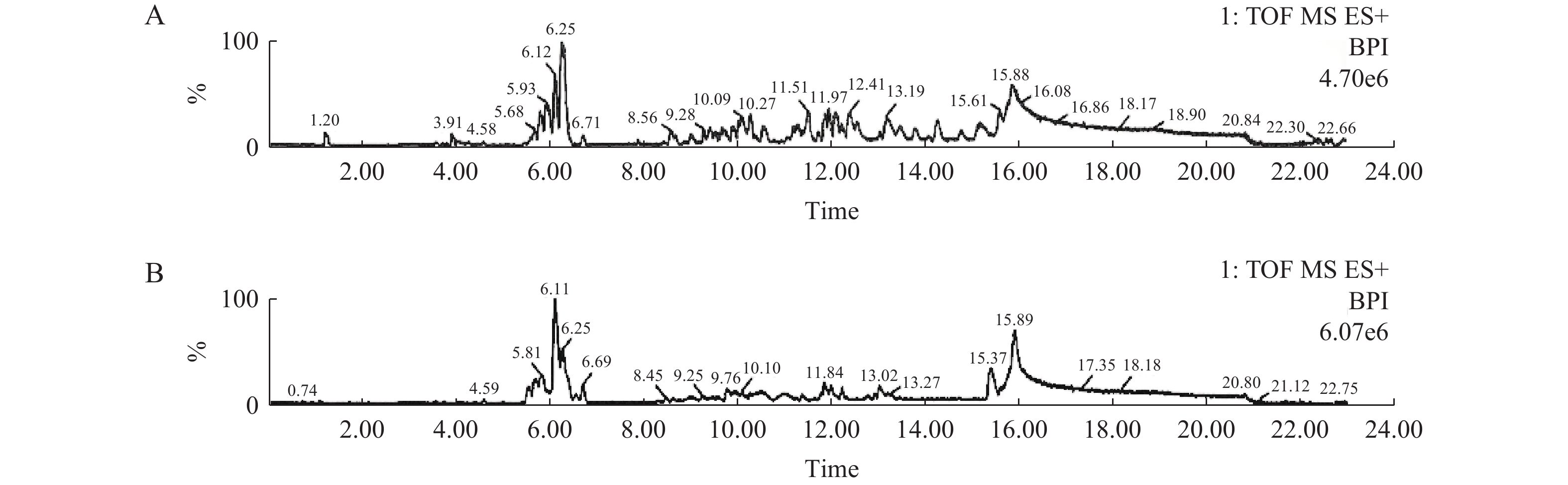
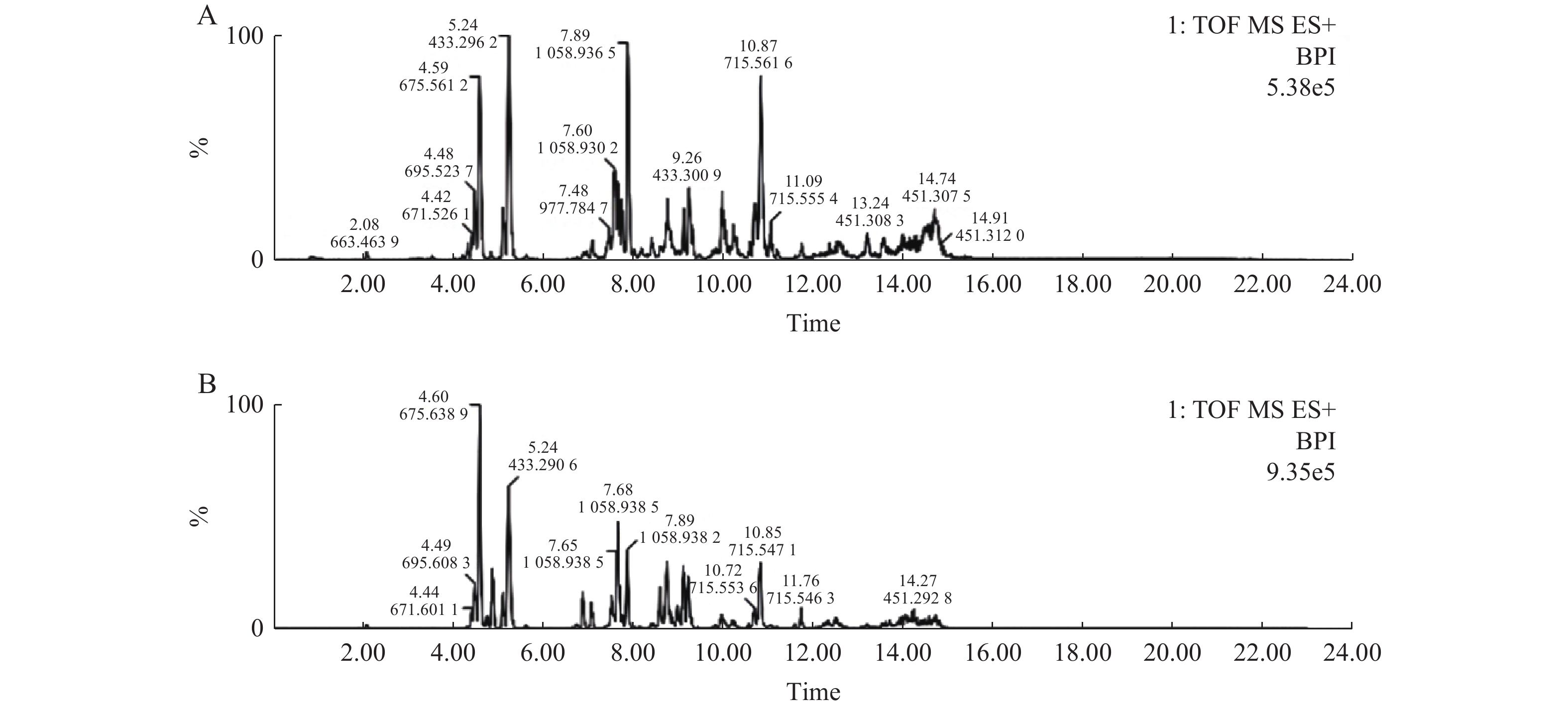
由图2、图3及图4分别可见,各牌号司盘、同牌号不同厂家司盘及同牌号不同生产工艺司盘间的总离子流图均存在差异,本研究所建立的方法可用于快速区分不同厂家、不同牌号、不同工艺等司盘样品,也可用于快速考察司盘的批间差异、批间稳定性等。
4. 讨论与展望
4.1 样品浓度
由于司盘类样品溶解性较差、较难电离,因此本研究司盘供试品质量浓度为3 mg/mL,远高于通常UPCC-QTOFMS所测定的样品浓度范围。为更好地维护仪器,可通过调整流动相、补偿溶剂比例、电压等方式,继续探索更为适宜的司盘类样品测定浓度。
4.2 色谱条件
近年来研究人员对吐温的组成、结构等研究越来越深入,但对与之结构类似的司盘组成研究仍鲜有报道[25−29]。在对O/W型表面活性剂司盘开展组分研究时,因其结构等与W/O型的吐温不同,需重新开发。各牌号司盘均在水中不溶、在醇中微溶,因此,为建立可行的色谱分析方法,尝试了各类常用试剂及不同试剂的组合,最终确定其可在混有一定量四氢呋喃的异丙醇中溶解。本研究建立的方法最终采用ESI为检测器,在开发此类方法时,通常不建议在流动相中使用四氢呋喃等正相溶剂。但受限于样品溶解情况,综合考虑仪器耐受情况及可能造成的电离影响等,最终仍在流动相中混入了5%的四氢呋喃,以保证样品溶解良好;同时考虑到四氢呋喃为极性的非质子溶剂,为使待测物更易电离,因此在补偿溶剂中加入了适量的甲酸溶液[30−31]。
4.3 展 望
本研究建立了采用UPCC-QTOFMS测定复杂药用辅料司盘的方法,可明确各司盘组成情况,用于复杂药用辅料质量控制、批间一致性的考察、不同来源样品的对比、原料考察及验收等工作,为进一步考察影响司盘理化性能、质量、安全性以及影响司盘与其他药物之间作用的关键质量属性提供了研究基础。本方法虽然更为绿色环保,但考虑到仪器价格等因素,也在持续开发及完善对应的HPLC方法,以提高方法可及性,后续广泛推广应用。
-
Table 1 Determination results of fatty acid composition of each brand of Span
Name of fatty acids Normalization results/% Span 20 Span 40 Span 60 Span 80 Span 85 Methyl caproate 0.1 / / / / Methyl caprylate 4.7 / / / / Methyl decanoate 5.4 / / / / Methyl laurate 52.5 / / 0.12 / Methyl myristate 19.9 / / 0.29 2.8 Palmitic acid methylester 9 99 47.1 4.97 4.3 Methylcis-9-hexadecenoate / / / / 4.8 Methyl stearate 5.3 / 48 1.54 1.1 Methyl oleate / / / 79.28 70.8 Methyl linolenate 2 / / 13.23 12.9 Table 2 Span 20 structure speculation
No. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 477.29 A Octanoic acid root,laurate root or decanoate root,laurate root 2 505.32 A Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,laurate root 3 533.35 A Decanoate root,myristic acid root or laurate root,laurate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root 4 561.39 A Laurate root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,palmitate root or octanoic acid root,stearate root 5 589.42 A Decanoate root,stearate root or laurate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,myristic acid root 6 351.19 B Laurate root and H 7 379.22 B Myristic acid root and H 8 733.53 C Octanoic acid root,decanoate,stearate root or octanoic acid root,laurate,palmitate or octanoic acid root,myristic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate,decanoate,palmitate or decanoate,laurate,myristic acid root or laurate,laurate,laurate 9 435.28 A Stearate root 10 789.59 C Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root,stearate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root,palmitate root or decanoate root,laurate root,stearate root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,palmitate root or laurate root,laurate root,palmitate root or laurate root,myristic acid root, myristic acid root 11 495.3 D Octanoic acid root,laurate root or decanoate root,decanoate root 12 523.33 D Octanoic acid root,myristic acid root or decanoate root,laurate root 13 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 14 551.36 D Decanoate root,myristic acid root or laurate root,laurate root or octanoic acid root,palmitate root 15 579.39 D Octanoic acid root,stearate root or decanoate root,palmitate root or laurate root,myristic acid root 16 607.42 D Decanoate root,stearate root or laurate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root ,myristic acid root 17 635.45 D Laurate root,stearate root or myristic acid root,palmitate root 18 313.14 E Octanoic acid root 19 341.17 E Decanoate root 20 369.2 E Laurate root 21 397.23 E Myristic acid root Table 3 Span 40 structure speculation
No. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 2 393.27 E Myristic acid root 3 901.71 C Myristic acid root,palmitate root,stearate root,laurate root,stearate root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root,palmitate root 4 791.53 C Octanoic acid root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,linoleic acid root or laurate root,laurate root,linoleic acid root 5 663.48 D Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root 6 425.26 E Palmitate root 7 631.50 A Laurate root,linoleic acid root Table 4 Span 60 structure speculation
No. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 673.51 A Palmitate root, stearate root 2 407.25 B Palmitate root and H 791.53 C Octanoic acid root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,myristic acid root,linoleic acid root or laurate root,laurate root,linoleic acid root 3 701.54 A Stearate root,stearate root C Octanoic acid root,octanoic acid root,linoleic acid root 4 435.28 B Stearate root and H 847.59 C Decanoate root,stearate root,linoleic acid root or decanoate root,oleate root,oleate root or laurate root,palmitate root,linoleic acid root 5 645.48 A Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root or aurate root,stearate root,stearate root 6 901.71 C Palmitate root,palmitate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,palmitate root,stearate root 7 929.74 C Myristic acid root,stearate root ,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root,stearate root 8 663.49 D Palmitate root,palmitate root or myristic acid root,stearate root 9 985.80 C Stearate root,stearate root,stearate root 10 957.78 C Palmitate root,stearate root ,stearate root C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root 11 425.26 E Palmitate root 12 691.52 D Palmitate root,stearate root 13 719.55 D Stearate root,stearate root Table 5 Span 80 structure speculation
No. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 671.49 A Oleate root,palmitate root A Linoleic acid root,linoleic acid root 2 695.49 A Oleate root,linoleic acid root D Oleate root,stearate root or stearate root,linoleic acid root 3 697.51 A Oleate root,oleate root D Stearate root,stearate root 4 431.25 B Linoleic acid root and H 5 433.27 B Oleate root and H 6 977.74 C Stearate root,linoleic acid root ,linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root 7 979.76 C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root ,oleate root,oleate root 8 715.52 D Oleate root,oleate root stearate root,linoleic acid root 9 713.5 D Oleate root,linoleic acid root Table 6 Span 85 structure speculation
No. m/z Parent nucleus structure Inferred R basis 1 643.46 A Myristic acid root,oleate root or palmitate root ,palm oil acid root 2 669.48 A Palmitatet,linoleic acid root or palm oil acid root ,oleate root 3 695.49 A Oleate root,linoleic acid root D Oleate root, stearate root 4 697.51 A Stearate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root ,oleate root D Stearate root 5 433.27 B Oleate root and H 6 715.52 D Stearate root,Linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root 7 979.76 C Stearate root,oleate root,linoleic acid root or oleate root,oleate root,oleate root 8 953.74 C Palmitate,stearate root ,linoleic acid root or palmitate root,oleate root,oleate root or palm oil acid root,oleate root,stearate root C Oleate root,linoleic acid root,linoleic acid root 9 641.45 A Myristic acid root,linoleic acid root D Myristic acid root,stearate root or palmitate root,palmitate root -
[1] Li J, Hu P, Xiao GL, et al. Analysis on influence factors affecting quality indexes of span 80[J]. Adv Fine Petrochem (精细石油化工进展), 2013, 14(2): 25-28. [2] LV Y. Synthesis and properties of SPAN-SA-COONa series surfactants [J]. Technol Innovation Newsletter(科技创新导报), 2014 (2): 115-116. [3] Pang YF, Xu MY, Lin S, et al. Research and market development of synthetic methods of non-ionic surfactants[J]. Appl Chem Ind (应用化工), 2023, 52(2): 546-550. [4] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia: part 4 (中华人民共和国药典: 四部) [S]. Beijing: China Medical [5] Liu WL, Liu W, Yin TT, et al. Preparation and characterization of W/O medium-chain fatty acid microemulsion[J]. Mod Food Sci Technol (现代食品科技), 2009, 25(5): 503-506. [6] Wang K, Xu ST, Xiao M, et al. Effects of span-80 on the properties of konjac glucomannan-zein blend films[J]. Sci Technol Food Ind (食品工业科技), 2016, 37(23): 267-271. [7] Zhang XF, Zhou ZC. New food additives Span and Twain [J]. Zhejiang Chem Ind (浙江化工), 1988 (3): 41-43. [8] Cheng BB. Application of food emulsifier compounding in food production [J]. Food Safety Guide(食品安全导刊), 2021 (24): 133, 135. [9] Li ZL. Evaluation of the immune effect of paratyphoid A flagellin combined with emulsion adjuvant on rabies vaccine [D]. Beijing: Beijing Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, 2019.
[10] Shi XG. Study on the preparation and effect of self-assembled nano vaccine [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020.
[11] Hou ZS, Zhu WW, Xiu YH. Recent progress in catalytic selective dehydration of sorbitol[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2015, 60(16): 1443-1451. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00030
[12] Bao Y, Wu CL, Ma JZ. Effect of emulsion method and co-emulsifier on performance of castor oil emulsion[J]. Chin Sur Det Cos(日用化学工业), 2012, 42(1): 39-42. [13] Li XM, Yu WQ, Zhang Y, et al. Advances in waters ACQUITY UPC2 and its methods establish[J]. Guangdong Chem Ind (广东化工), 2020, 47(6): 103-105,94. [14] Wang Y, Ju ZC, Li LN, et al. A complementary chromatographic strategy for integrated components characterization of Imperatae Rhizoma based on convergence and liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry and molecular network[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2022, 1678(2022): 463342.
[15] Zhu RY, Xu XF, Shan QY, et al. Determination of differentiating markers in coicis Semen from multi-sources based on structural similarity classification coupled with UPCC-xevo G2-XS QTOF[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 549181. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.549181
[16] Yang GY, Liang QY, Yang S, et al. Determination of 19 sex hormones in health foods by ultra performance convergence chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with pass-through solid phase extraction[J]. Food Sci (食品科学), 2022, 43(20): 370-376. [17] Hu S, HuaZD, HuangY, et al. Fast separation and detection of fentanyls isomers by ultra performance convergence chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Anal Chem (分析化学), 2022, 50(6): 964-972. [18] Li P, Yao CL, Zhang JQ, et al. Analysis of the lipids of Descurainiae Semen and Lepidii Semen based on three chromatography tandem mass spectrometry techniques[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2023, 54(2): 484-497. [19] SongY, Guan YY, Zou ZF, et al. Determination of butylhydroxyanisole and dibutylhydroxytoluene in vegetable oil by ultra performance convergence chromatography[J]. Occupation Health(职业与健康), 2016, 32(3): 328-331. [20] Ding JY, Liu FG, Wng H, et al. Determination of R-valsartan in valsartan active pharmaceutical ingredients by ultra performance convergence chromatography [J]. Analy Test Tech Instruments(分析测试技术与仪器), 2022, 28 (4):405-410. Ding JY, Liu FG, Wng H, et al. Determination of R-valsartan in valsartan active pharmaceuticalingredients by ultra performance convergence chromatography [J]. Analy Test Tech Instruments(分析测试技术与仪器), 2022, 28(4):405-410.
[21] Zhu WX, Yang R, Xu YW, et al. Qualitative analysis of medium/long chain triglyceride composition by ultra performance convergence chromatography tandem quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Chin Pharm J(中国药学杂志), 2016, 51(15): 1324-1329. [22] Zhang XH, Qi C, Tao GJ, et al. Rapid analysis of triglyceride composition in Vegetable oils by ultra performance convergence chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Chin Oils Fats, 2018, 43(11): 127-132.
[23] Li T, Wang J, Yuan M, et al. Analysis of UPCC-Q-TOF-MS components and safety of polyoxyethylene 35 castor oil[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2020, 55(11): 2688-2694. [24] Wu WY. Study on the material basis of traditional Chinese medicine based on UPCC / Q-TOF MS technology [C]. // Proceedings of the 10th Shanghai International Conference on Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Medicine(第十届上海中医药与天然药物国际大会论文集). 2017: 35-36. [25] ZhouY, Zhao X, Hu N, et al. A method for rapid analysis of polysorbate 80 components[J]. J Chin Pharm Univ(中国药科大学学报), 2022, 53(2): 192-199. [26] Yang K, Han XL. Accurate quantification of lipid species by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry - Meet a key challenge in lipidomics[J]. Metabolites, 2011, 1(1): 21-40. doi: 10.3390/metabo1010021
[27] Schwartzberg LS, Navari RM. Safety of polysorbate 80 in the on c ology setting[J]. Adv Ther, 2018, 35 (6): 754-767.
[28] Puschmann J, Evers DH, Müller-Goymann CC, et al. Development of a design of experiments optimized method for quantification of polysorbate 80 based on oleic acid using UHPLC-MS[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2019, 1599(2019): 136-143.
[29] Wang J, Xu K, Yang Y, et al. Establishment of fingerprints and identification method of polysorbates[J]. China Pharm (中国药业), 2023, 32(6): 55-60. [30] E GY. Simulation and optimization of tetrahydrofuran recovery system in pharmaceutical waste liquid [J]. Chem Indus Manag(化工管理), 2017 (35): 236. [31] Zhao B. Mass spectrometry study on the conformation of superoxide dismutase and its interaction with small molecules [D]. Anhui: University of Science and Technology of China, 2019.



 下载:
下载: